一方面,色彩空间根据不同的着色方法(例如,添加一些三原色),包含一定数量的具有离散间隔的唯一指定色彩,例如 RGB、CMYK 或 CIE-L*a*b*。
另一方面,有些色彩目录并不总是基于明确的分类方案;它们只是任意命名的色彩集合,只能再现某个色彩空间(如 RAL 或 PMS 系统)中的一个子集。
因此,不可能不加区分地将色彩空间(如 RGB)中的任何颜色映射到色彩系统(如 PMS)中的命名颜色上。该系统中可能不存在相应的颜色,因此必须找到最接近的颜色或最接近的颜色之一。
RAL 颜色
RAL 颜色是在全球范围内使用的一系列颜色系统和颜色目录,每个系统和目录都包括一个由 RAL GmbH 创建和管理的标准化颜色调色板(数字和印刷)。在日常语境中,当人们谈论 RAL 颜色时,通常指的是 RAL Classic 颜色目录。该目录是一个颜色集合,随着时间的推移而不断演变,主要是根据行业要求开发的(主要用于油漆和粉末涂料,不过现在也有用于塑料的目录)。
潘通配色系统
Pantone Matching System(PMS)是国际通用的色彩系统名称,由 Pantone LLC 于 1963 年开发,主要用于制图和印刷行业。它包括传统四色印刷无法实现的特殊颜色,并为每种颜色分配了独特的数字标识符。
RGB 色彩
该色彩空间用于在屏幕、移动设备等上表示色彩。
•RGB 是一种加色法色彩系统,即把不同的颜色混合在一起。
•三原色(红、绿、蓝)各分为 256 个亮度等级。这意味着通过组合可以产生 16,777,216 种不同的色调。
•使用的颜色越多,效果就越鲜艳。
CMYK 色彩
该色彩空间用于表示印刷品中的色彩。
•CMYK 是一种减色法色彩系统,即减去三个主要成分(青色、洋红色、黄色)和黑色成分(基调)来产生不同的颜色。
•黑色成分是产生灰色和深黑色的必要条件。
•使用的颜色越少,效果越亮。
实验室颜色
L*a*b* 色彩空间(又称:CIELAB)使用笛卡尔坐标系来描述所有可感知的颜色。L*a*b* 色彩模型最重要的特点是不依赖于任何设备,并且与感知相关。这意味着,无论色彩是如何生成或复制的,色彩的定义都是标准观察者在正常光线条件下感知到的色彩。
在这里,L(亮度)代表色彩空间中颜色的亮度。0 表示纯黑,100 表示纯白。a 值表示颜色在红绿轴上的位置,负值表示偏离零点的绿色方向,正值表示偏离红色方向。b 值表示色相在黄蓝轴上的位置(负值表示蓝色,正值表示黄色)。CIELab 公式在 DIN/EN/ISO 标准 11664-4 中有明确定义。
色彩空间和色彩系统的比较。
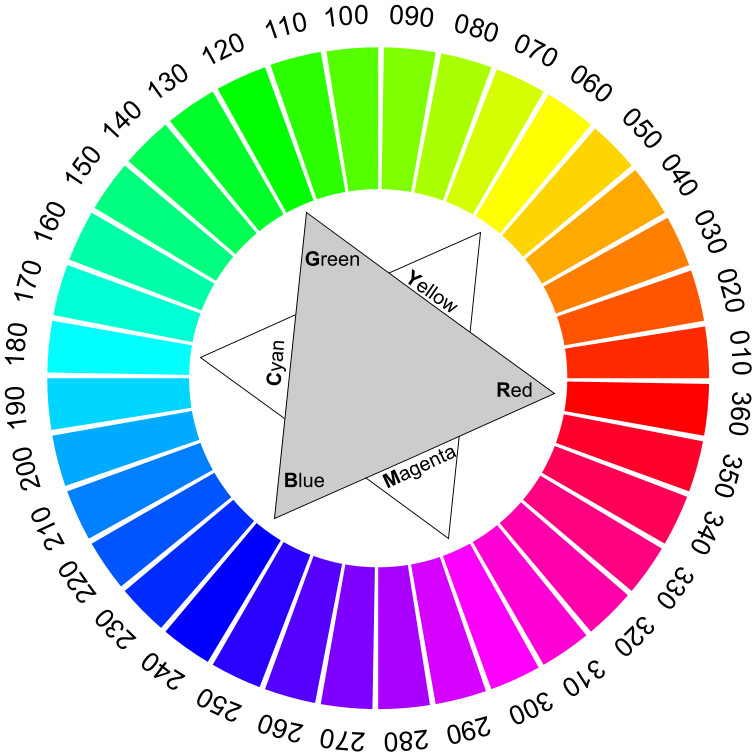
比较的起点是 HSB 色彩空间,它是许多色彩模型的基础,符合色彩测量和摄影技术再现的要求。颜色是通过色彩空间中的三个坐标来定义的:
•色调(色相):色轮上的色角(0° 代表红色,120° 代表绿色,240° 代表蓝色)
•饱和度(饱和度):(0% = 中性灰,50% = 低饱和度色彩,100% = 饱和纯色)
•亮度(亮度):(0% = 无亮度,100% = 全亮度)
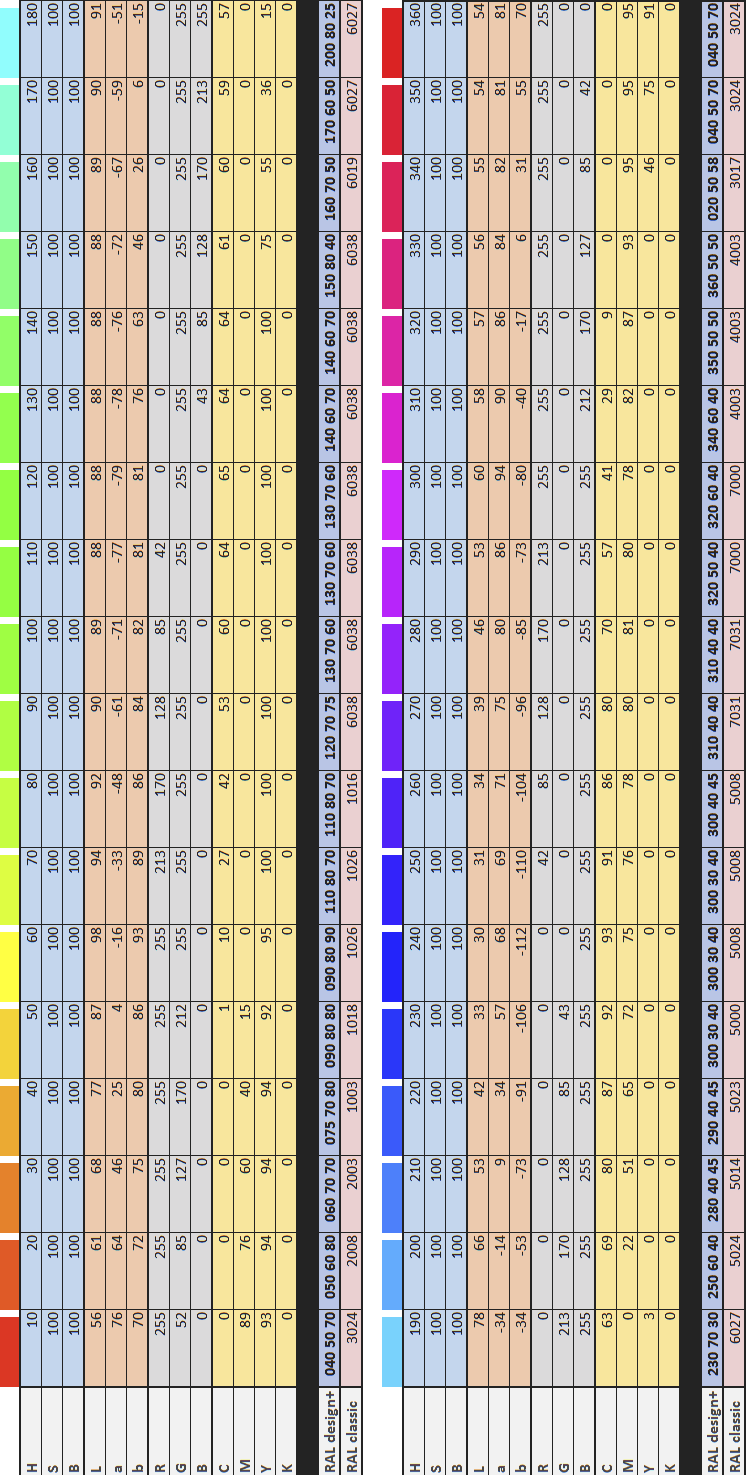
使用 HSB 色轮进行比较,在色轮上,不同的基色(色调 H)在各自的最高色彩饱和度 (S) 和最大亮度 (B) 下以递增色调(36 个色调值,以 10° 为增量)进行指定。根据得出的 L*a*b* 值,为每个指定的色彩空间和色彩系统指出最接近的颜色。由于色彩目录通常包含更多柔和的色彩,因此 S 和 B 值永远不会太高,因此色彩目录之间的差异会更加明显。
由于无法将 RAL 直接转换为 RGB 或 CMYK,因此下表应视为近似值。
On one side, there are color spaces that, based on the use pf different coloration methods (for example, the addition of a few primary colors), contain a defined quantity of uniquely assigned colors with discrete intervals, such as RGB, CMYK or CIE-L*a*b*.
On the other side, there are color catalogs that are not always based on a clear classification scheme; they are only arbitrary collections of named colors that only ever reproduce a subset of colors within a color space, for example, the RAL or PMS systems.
Therefore, it is not possible to indiscriminately map any color at all from a color space (e.g. from RGB) onto a named color from a color system (e.g. from PMS). It is possible that a corresponding color may not exist in that system, so it is necessary to find the nearest color or one of the nearest colors.
RAL colors
RAL colors are a range of color systems and color catalogs used worldwide, each including a palette of standardized colors (digital and printed), which are created and managed by RAL GmbH. When people talk about RAL colors in an everyday context, they generally mean the color catalog RAL Classic. This catalog is a collection of colors that has evolved over time and was primarily developed according to industry requirements (mainly for painting and powder coating, although there is also a catalog for plastics nowadays).
Pantone Matching System
Pantone Matching System (PMS) is the name of an internationally used color system that was developed by Pantone LLC in 1963 and is mainly used in the graphic arts and printing industries. It includes special colors that cannot be achieved with conventional four-color printing, and assigns unique numeric identifier to each of these colors.
RGB colors
This color space is used to represent colors on screens, mobile devices, etc.
•RGB is an additive color system, meaning that it mixes different colors together.
•Each of the 3 primary colors (Red, Green, Blue) is divided into 256 brightness levels. This means that 16,777,216 different hues are possible through combinations.
•The more color(s) is/are used, the brighter the result.
CMYK colors
This color space is used to represent colors in print.
•CMYK is a subtractive color system, meaning that it subtracts the 3 main components (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow) and the black component (Key) to create different colors.
•The black component is required to create shades of gray and deep black.
•The less color(s) is/are used, the brighter the result.
Lab colors
The L*a*b* color space (also known as: CIELAB) uses a Cartesian coordinate system to describe all perceptible colors. Among the most important features of the L*a*b* color model are the fact that is not dependent on any device and the fact that it is related to perception. This means that colors are defined as they are perceived by a standard observer under normal light conditions, regardless of how they are generated or reproduced.
Here, L (Lightness) stands for the brightness of a color in the color space. 0 indicates a pure black, an L value of 100 corresponds to a pure white. The a value describes a color's position on the red-green axis, where negative values represent deviation from the zero point in the green direction and positive values represent deviation in the red direction. The b value represents the position of a hue on the yellow-blue axis (negative values for blue, positive values for yellow). The gray point or neutral point in the CIELab model is located at a = b = 0. The CIELab formula is explicitly defined in the DIN/EN/ISO standard 11664-4.
Comparison of color spaces and color systems.
The starting point for a comparison is the HSB color space, which forms the basis of many color models and is geared towards the requirements of colorimetry and photo-technical reproduction. A color is defined by means of three coordinates in the color space:
•Hue (hue): Color angle on the color wheel (0° for red, 120° for green, 240° for blue)
•Saturation (saturation): (0% = neutral gray, 50% = low-saturation colors, 100%= saturated, pure colors)
•Brightness (brightness): (0% = no brightness, 100% = full brightness)
The comparison is done with a HSB color wheel, on which different base colors (hue H) are specified at their respective highest color saturation (S) and maximum brightness (B) in ascending hues (36 hue values in 10° increments). On the basis of the resulting L*a*b* values, the closest colors are indicated for each of the specified color spaces and color systems. There can be a more noticeable difference between color catalogs since color catalogs generally contain more muted colors, so S and B are never too high.
The following table should be taken as an approximation since direct conversion from RAL to RGB or CMYK is not possible.